What Are Large Language Models and Why Are They Crucial to Generative AI?
Authored by Matthew Kanterman and ChatGPT
Large language models (LLMs) sit at the core of generative artificial intelligence (GAI) applications. But amid this rapidly evolving technology and alphabet soup of different models, some are wondering just what they are, how they impact GAI and how to differentiate some of the leading LLMs from each other. Let’s break it down.
What Are Large Language Models?
A large language model is an artificial intelligence model that has been trained on a massive amount of data to generate natural language responses to given prompts. These models are typically based on neural network architectures, such as the transformer architecture, and have millions or even billions of parameters.
How Are Large Language Models Used in Generative AI?
Large language models are used in generative AI applications to generate new text that is coherent, contextually relevant, and similar in style and tone to the input text. The models achieve this by learning the statistical patterns and relationships between words and phrases in natural language text through a process called pre-training.
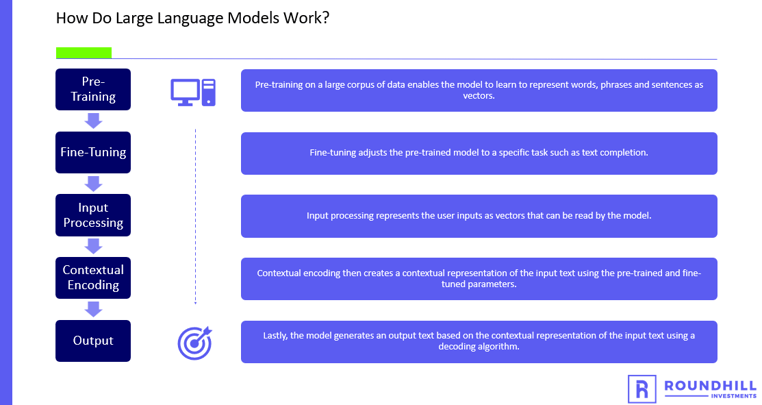
Source: ChatGPT, May 8, 2023
Once pre-trained, these models can be fine-tuned on specific tasks to optimize their performance for specific applications, such as chatbots, content creation tools, or language translation services. For example, a chatbot that uses a large language model might take a user's input text as a prompt and generate a response based on the statistical patterns it has learned from its pre-training.
What Are Some Leading Examples of Large Language Models?
Here’s a selection of some of the leading LLMs, their creators and the number of parameters on which they are trained.
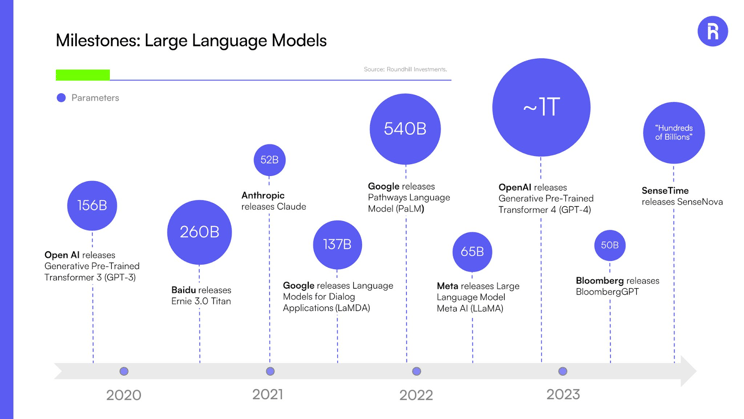
Source: Roundhill Investments, May 10, 2023
Some of the most popular LLMs include the Generative Pre-Trained Transformer models (GPT) that power OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Microsoft’s Bing AI search. GPT-4 is the latest version of this model, with approximately 1 trillion parameters.
Google has launched several LLMs, including LaMDA and PaLM that have 137 billion and 540 billion parameters, respectively. It’s also invested in Anthropic, who has released the Claude model with 52 billion parameters.
Baidu’s Ernie 3.0 Titan model, used to power its ErnieBot chatbot, has 260 billion parameters. Chinese AI peer SenseTime’s SenseNova model, used to power its SenseChat chatbot and other services such as a text-to-image tool, has hundreds of billions of parameters.
Bloomberg built a finance-specific model called BloombergGPT with 50 billion parameters.
This document does not constitute advice or a recommendation or offer to sell or a solicitation to deal in any security or financial product. It is provided for information purposes only and on the understanding that the recipient has sufficient knowledge and experience to be able to understand and make their own evaluation of the proposals and services described herein, any risks associated therewith and any related legal, tax, accounting or other material considerations. To the extent that the reader has any questions regarding the applicability of any specific issue discussed above to their specific portfolio or situation, prospective investors are encouraged to contact Roundhill Investments or consult with the professional advisor of their choosing.
Investing involves risk, including possible loss of principal. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Companies and other companies that rely heavily on technology are particularly vulnerable to research and development costs, substantial capital requirements, product and services obsolescence, government regulation, and domestic and international competition, including competition from foreign competitors with lower production costs. Stocks of such companies, especially smaller, less-seasoned companies, may be more volatile than the overall market. AI Companies may face dramatic and unpredictable changes in growth rates. AI Companies may be targets of hacking and theft of proprietary or consumer information or disruptions in service, which could have a material adverse effect on their businesses.